Abstract
BACKGROUND
In the RESPONSE study, rux (a potent JAK1/2 inhibtor) has demonstrated superior response as compared to best available therapy (BAT) in controlling hematocrit (Hct), and improving splenomegaly and symptoms in PV pts who were inadequately controlled with HU. An expanded-access phase 3b study has been designed to provide rux treatment to pts who are HU resistant/intolerant, have no other treatment options available and are not eligible for any ongoing clinical trial in PV. The present analysis reports the safety and efficacy of rux in pts enrolled in the study who received rux for at least 6 months (mo) or discontinued prematurely.
METHODS
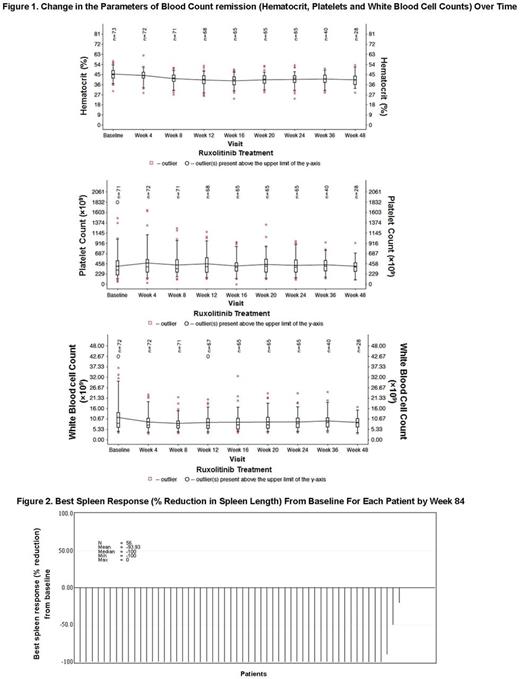
Pts with PV who were HU resistant/intolerant were included in this global, single-arm, open-label, multicenter, expanded-access phase 3b study. Eligible pts received rux at a starting dose of 10 mg bid and pts were required to visit clinic every 4 weeks (wks) until wk 24 and every 12 wks thereafter. Dose adjustments were allowed up to a maximum of 25 mg bid. The primary endpoint was to assess the safety of rux. Secondary endpoints included change in Hct, change in spleen length from baseline (BL), change in symptom scores from BL as assessed by MPN-SAF TSS, and pt-reported outcomes. Hct control and blood count remission were defined as absence of phlebotomy (PBT) eligibility starting at wk 8 and continuing through wk 24, with no more than 1 PBT eligibility occurring after first dose date and prior to wk 8; and absence of PBT eligibility, platelet count ≤ 400 × 109/L, a white blood cell (WBC) count ≤ 10 × 109/L, respectively. PBT eligibility was defined as confirmed Hct > 45%, at least 3 percentage points higher than the BL Hct or confirmed Hct > 48%. The final analysis will be performed when all pts had been followed for 30 days after the completion of treatment.
RESULTS
A total of 75 enrolled pts [HU resistant (43%) and HU intolerant (57%)] were evaluable at the time of data cutoff (January 15, 2017). The median age was 68 years (range, 33-89) and 60% were male. Median time since the diagnosis of PV was 65.3 mo (range, 5.4-396.8). The mean (SD) Hct, WBC, platelet counts and spleen length below costal margin at BL were 45.4% (5.10), 12.0 × 109/L (8.56), 471.6 × 109/L (493.99) and 2.76 cm (3.1), respectively. 11%, 7%, and 51% of pts had received 1, 2, or ≥ 3 PBTs in the 52 wks prior to screening. 28% of pts had a prior thromboembolic event and 8% had a nonmelanoma malignant skin lesion.
At data cutoff, 21 pts (28%) were ongoing, 40 pts (53%) had completed treatment as per protocol, including transition to commercial drug, and 14 pts (19%) discontinued prematurely. Primary reasons for discontinuation included AE (12%), pt decision (1%), withdrawal of consent (1%), disease progression (3%), and death (1%, investigator assessed it as not related to the study drug). The median exposure was 43.3 wks (range, 1-72), and median dose intensity of rux was 20.0 mg/day (range, 8.9-45.4). Adverse events (AEs) led to a change in dose in 44% of pts. All the AEs leading to rux discontinuation occurred at a frequency of < 2%. Anemia (all grades, n = 16; grade 3 or 4, n = 1) was the most common hematologic AE. Most frequent nonhematologic AEs (> 10%) were constipation, fatigue, asthenia, headache, and pruritus. Frequency of all grades thromboembolic events (SMQ) was 4% (n = 3) and grade 3/4 was 1% (n = 1). All grades malignant melanoma, leiomyoma, transformation to myelofibrosis and acute myeloid leukemia, and marginal zone lymphoma occurred in 1 pt each, and basal cell carcinoma in 3 pts.
At wk 24, 52 pts (69% [95% CI, 58%-80%]) achieved Hct control. Of the 52 pt achieving Hct control, 24 were HU resistant and 28 were HU intolerant. Blood count remission was seen in 17 pts (23%, [95% CI, 4%-34%]) (Figure 1), where 7 pts were HU resistant and 10 were HU intolerant. At wk 24, number of PBTs received in the previous 4 wks were reduced to 2 from 14 received between screening and BL visits. Best spleen response from BL for each pt by wk 84 is shown in Figure 2. Approximately, 36% (21 of 59) and 45% (34 of 75) of pts experienced ≥ 50% reduction in MPN-SAF TSS from BL at wk 24 and at any time, respectively.
CONCLUSION
At wk 24 in this study, pts treated with rux experienced benefits in terms of Hct control, hematologic remission, and reduction in spleen size and symptom score consistent with those seen in previous clinical trials of rux in pts with PV. The safety and efficacy data from present study are consistent with the findings from RESPONSE and RESPONSE-2 studies.
Devos: Novartis: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy. Leber: Novartis Canada: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene Canada: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Almeida: Bristol Meyer Squibb: Honoraria; Alexion: Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Ranta: Novartis: Consultancy. Kiladjian: AOP Orphan: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Chrit: Novartis: Employment. Yin: Novartis: Employment. Perez Ronco: Novartis Pharma AG: Employment. Foltz: Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.